数据包和结构体
本章节内容从数据包
udp
使用python脚本发送udp数据包
import socket
# 目标IP和端口
target_ip = "192.168.100.66"
target_port = 1024
# 本地IP和端口
local_ip = "192.168.100.33"
local_port = 1024
# TTL值(最大跳数)
ttl = 128
# 创建UDP socket
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
sock.setsockopt(socket.IPPROTO_IP, socket.IP_TTL, ttl)
# 绑定到本机IP和端口(如果需要)
sock.bind((local_ip, local_port))
# 要发送的数据
message = "Hello"
# 发送数据
sock.sendto(message.encode(), (target_ip, target_port))
# 关闭socket
sock.close()
执行python脚本
python udp_send.py
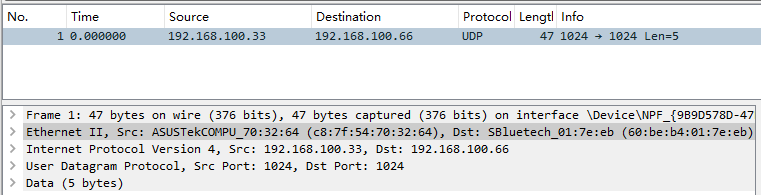
以太网头
以太网i王头:包含目的MAC,源MAC和帧类型。
帧类型表示后面数据的类型,对于ip包来说是0x0800
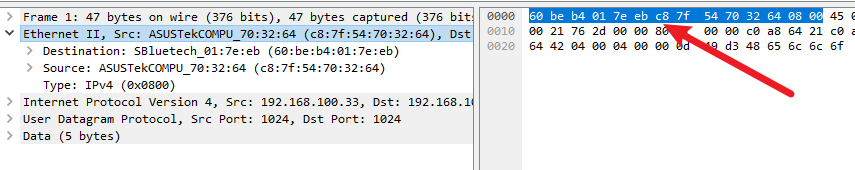
dpdk中的以太网头
// 头文件为 rte_ether.h
struct rte_ether_hdr {
struct rte_ether_addr dst_addr; /**< Destination address. */
struct rte_ether_addr src_addr; /**< Source address. */
rte_be16_t ether_type; /**< Frame type. */
} __rte_aligned(2);
常见的帧类型:
/* Ethernet frame types */
#define RTE_ETHER_TYPE_IPV4 0x0800 /**< IPv4 Protocol. */
#define RTE_ETHER_TYPE_ARP 0x0806 /**< Arp Protocol. */
#define RTE_ETHER_TYPE_VLAN 0x8100 /**< IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging. */
示例
struct rte_ether_hdr *ehdr = rte_pktmbuf_mtod(mbuf, struct rte_ether_hdr *);
if (ehdr->ether_type != rte_cpu_to_be_16(RTE_ETHER_TYPE_IPV4))
{
continue;
}
ip头
包含源ip,目的ip,ttl,包长,协议类型等
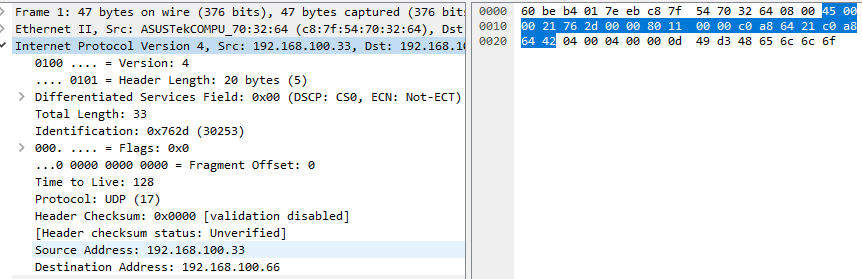
dpdk中的ip头
/**
* IPv4 Header, rte_ip.h
*/
struct rte_ipv4_hdr {
uint8_t version_ihl; /**< version and header length */
uint8_t type_of_service; /**< type of service */
rte_be16_t total_length; /**< length of packet */
rte_be16_t packet_id; /**< packet ID */
rte_be16_t fragment_offset; /**< fragmentation offset */
uint8_t time_to_live; /**< time to live */
uint8_t next_proto_id; /**< protocol ID */
rte_be16_t hdr_checksum; /**< header checksum */
rte_be32_t src_addr; /**< source address */
rte_be32_t dst_addr; /**< destination address */
} __attribute__((__packed__));
常见协议类型
#define IPPROTO_ICMP 1
#define IPPROTO_IPV4 4
#define IPPROTO_TCP 6
#define IPPROTO_UDP 17
示例
struct rte_ipv4_hdr * iphdr = rte_pktmbuf_mtod_offset(mbuf, struct rte_ipv4_hdr *, sizeof(struct rte_ether_hdr));
if (iphdr->next_proto_id != IPPROTO_UDP)
{
continue;
}
udp头
源端口,目的端口,长度,校验和
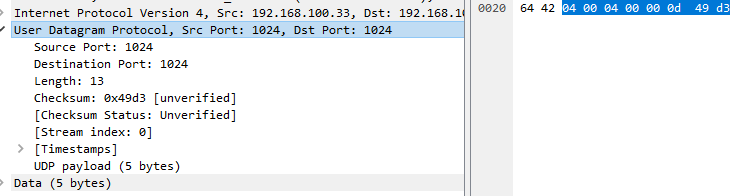
dpdk中的udp头
/**
* UDP Header, rte_udp.h
*/
struct rte_udp_hdr {
rte_be16_t src_port; /**< UDP source port. */
rte_be16_t dst_port; /**< UDP destination port. */
rte_be16_t dgram_len; /**< UDP datagram length */
rte_be16_t dgram_cksum; /**< UDP datagram checksum */
} __attribute__((__packed__));
示例
// Print 5 bytes of UDP payload (without checking the packet is UDP).
// (ether header) 14 + (ip header) 20 + (udp header) 8 = 42
char const *pack_data = rte_pktmbuf_mtod(mbufs[i], char const *);
for (int j = 42; j < 47; j++) {
putchar(pack_data[j]);
}
putchar('\n');
示例2:
struct rte_ipv4_hdr * iphdr = rte_pktmbuf_mtod_offset(bufs[i], struct rte_ipv4_hdr *, sizeof(struct rte_ether_hdr));
if (iphdr->next_proto_id == IPPROTO_UDP)
{
struct rte_udp_hdr *udphdr = (struct rte_udp_hdr *)(iphdr+1);
uint16_t length = udphdr->dgram_len;
*(char *)(udphdr + length-1) = '\0';
printf("udp: %s\n", (char *)(udphdr+1));
}
icmp
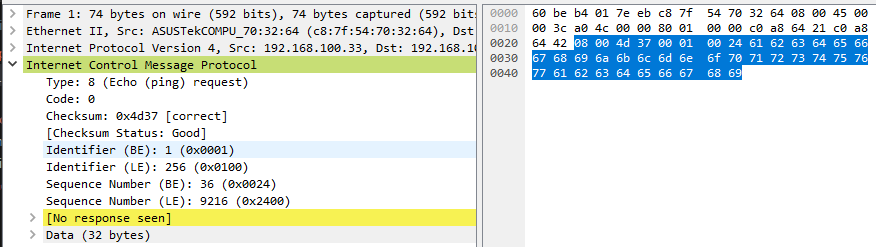
dpdk中的icmp头
/**
* ICMP Header, rte_icmp.h
*/
struct rte_icmp_hdr {
uint8_t icmp_type; /* ICMP packet type. */
uint8_t icmp_code; /* ICMP packet code. */
rte_be16_t icmp_cksum; /* ICMP packet checksum. */
rte_be16_t icmp_ident; /* ICMP packet identifier. */
rte_be16_t icmp_seq_nb; /* ICMP packet sequence number. */
} __rte_packed;
icmp 包类型
/* ICMP packet types */
#define RTE_IP_ICMP_ECHO_REPLY 0
#define RTE_IP_ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST 8
示例
解析收到的icmp请求
struct rte_ipv4_hdr * ip_hdr = rte_pktmbuf_mtod_offset(mbuf, struct rte_ipv4_hdr *, sizeof(struct rte_ether_hdr));
if (ip_hdr->next_proto_id != IPPROTO_ICMP){
printf("proto id not icmp 1\n");
return ;
}
struct rte_icmp_hdr *icmp_hdr = (struct rte_icmp_hdr *)(ip_hdr+1);
printf("boi ICMP Packet: \n");
printf(" Type: %u\n", icmp_hdr->icmp_type);
printf(" Code: %u\n", icmp_hdr->icmp_code);
对icmp请求进行回复
ip_h = (struct rte_ipv4_hdr *) ((char *)eth_h + l2_len);
icmp_h = (struct rte_icmp_hdr *) ((char *)ip_h +
sizeof(struct rte_ipv4_hdr));
if (! ((ip_h->next_proto_id == IPPROTO_ICMP) &&
(icmp_h->icmp_type == RTE_IP_ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST) &&
(icmp_h->icmp_code == 0))) {
rte_pktmbuf_free(pkt);
printf("now icmp\n");
return NULL;
}
rte_ether_addr_copy(ð_h->src_addr, ð_addr);
rte_ether_addr_copy(ð_h->dst_addr, ð_h->src_addr);
rte_ether_addr_copy(ð_addr, ð_h->dst_addr);
ip_addr = ip_h->src_addr;
if (is_multicast_ipv4_addr(ip_h->dst_addr)) {
uint32_t ip_src;
ip_src = rte_be_to_cpu_32(ip_addr);
if ((ip_src & 0x00000003) == 1)
ip_src = (ip_src & 0xFFFFFFFC) | 0x00000002;
else
ip_src = (ip_src & 0xFFFFFFFC) | 0x00000001;
ip_h->src_addr = rte_cpu_to_be_32(ip_src);
ip_h->dst_addr = ip_addr;
ip_h->hdr_checksum = ipv4_hdr_cksum(ip_h);
} else {
ip_h->src_addr = ip_h->dst_addr;
ip_h->dst_addr = ip_addr;
}
icmp_h->icmp_type = RTE_IP_ICMP_ECHO_REPLY;
cksum = ~icmp_h->icmp_cksum & 0xffff;
cksum += ~RTE_BE16(RTE_IP_ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST << 8) & 0xffff;
cksum += RTE_BE16(RTE_IP_ICMP_ECHO_REPLY << 8);
cksum = (cksum & 0xffff) + (cksum >> 16);
cksum = (cksum & 0xffff) + (cksum >> 16);
icmp_h->icmp_cksum = ~cksum;